origin of petroleum
Origin
of petroleum
Millions
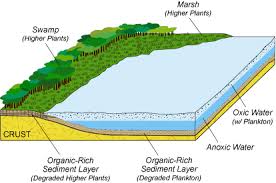
of years ago, the earth was populated with plants and animals. Much of
that life was located in or adjacent to ancient rivers, lakes, and sea. As
plants and animals died, their remains settled to the bottom of these bodies of
water. Ancient rivers carried mud and sand that buried the organic
material. As layers of organic material continued to build up, the oxygen
supply to the lower layers eventually was cut off and decomposition slowed
down. The thickness of such layers grew to 100s of feet over the time.
Introduction
Petroleum is a Latin
word of (Petra ‘‘rock’’ + Oleum ‘’ oil ‘’), It is completely
different than oil
that comes from vegetable sources such as the olive, but modern research
has traced its origin to the lipids (oils) of plank tonic (free floating) plants
and animals which live in brackish water such as blue-green algae's and
foraminifera. The brackishness is essential because aerobic bacteria do not
live in brackish water which in turn would decompose all of the organic
matter. In brackish water the organic matter of the planktonic plants and
animals sinks to the bottom and incorporated into clay sediments which
ultimately become sedimentary rocks, as we called shale rock. Under high
pressure and temperature the oil of clay shale's can be squeezed out and into
porous rock. In porous rock the oil can travel, until it reaches an impervious
barrier such as a salt dome.
Petroleum is so important to ensure life
sustainability as a source of energy which has a big impact on society from
several aspects including: economy, politics and human basic needs. It is
a strategic commodity that every country is seeking by developing new
technologies which contribute to maximising petroleum recovery from under grounded.
Origin of petroleum dilemma
The origin of petroleum
still has uncertainties despite the tremendous researches and studies devoted
to it rather than any other natural substance. There are two different
theories for the origin of petroleum; Organic and Inorganic origin.
Inorganic or ABiotic origin
States that hydrogen and
carbon came together under great temperature and pressure, far below the
earth’s surface and formed oil and gas where chemical reactions have occurred.
The oil and gas then seeped through porous rock to deposit in various natural
underground traps .It has also excluded the hypothesis that petroleum is a
finite substance. There are some different theories that describe the inorganic
origin of petroleum which include.
Metal carbide
theory
Developed by a Russian chemist
and states that the deposition of petroleum is controlled by tectonic
activities that occurred during the life of sedimentary rock. To explain his
observations, he has put forth "metal carbide theory". Metal
carbides deep in Earth reacted with water at high pressure and temperature
to form acetylene which condenses to heavier hydrocarbons.
Reaction equation is: Cac2+H2O=
C2H2+Ca(OH)2
Volcanic theory
Involves out gassing of the mantle via
volcanic activity or eruption.
Earthquake theory
Involves
out gassing deep Earth's mantle via tectonic activities such as faults, and
this is still happening till now.
Sentimentalization theory
States that hydrocarbon is a
by-product that came from a metamorphic transformation of the green dark
Olivine mineral ,which was found in
Earth's mantle.
Overwhelming evidences for inorganic origin of petroleum
§ Geographical location: most of hydrocarbon producing regions are located close
to belts of tectonic activities.
§ Stability with depth: Corresponding to what organic theory's supporters have
admitted themselves, petroleum is a fossil fuel, and there has never been
a real fossil found below 16000 feet. Nowadays, there is drilling for oil
reservoirs at 28000 feet or 30000 feet where there is no a
fossil remains.
Organic origin
It is the most widely
accepted. The oil and gas are formed from remains of prehistoric plants and
animals. Remains of plants have been transformed to coal and
animals to oil and gas. These remains were settled into seas and
accumulated at the ocean floor and buried under several kilo meters of
sediments. Over a few million years, the layers of the organic
material were compressed under the weight of the sediments above them. The increase
in pressure and temperature with the absence of oxygen changed the mud,
sand, slit or sediments into rock and organic matter into Kerosene . After
further burial and heating, the kerosene transformed via cracking into
petroleum and natural gas.
Overwhelming evidences for organic origin of petroleum
§ Presence of brine (sea water) with petroleum.
§ Petroleum is found only in association with sedimentary rocks.
There is no petroleum associated with igneous or metamorphic rocks.
§ Polarised light passing through all petroleum resources
undergoes a rotation that is similar to all organic oils.
§ Molecules in hydrocarbons are thought to be similar to that of
the organic matter.
§ The organic carbon found in plants is depleted into C13 due to photosynthesis process. In dead
organic matter, it is further depleted due to radioactive
decaying. The same depletion was found in petroleum and natural gas.



Comments
Post a Comment